
Both methods rely on x-ray radiographic examination of the hand and wrist. It is generally determined on the basis of the Greulich and Pyle (GP) atlas ( 1) or the Tanner-Whitehouse method (TW2) ( 2). © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.īONE AGE ASSESSMENT is requested in many clinical situations to evaluate skeletal development. Data from this study may be useful to develop an atlas of skeletal development and bone age. Conclusionĭetermination of bone age with MRI is feasible and shows good interobserver reproducibility.
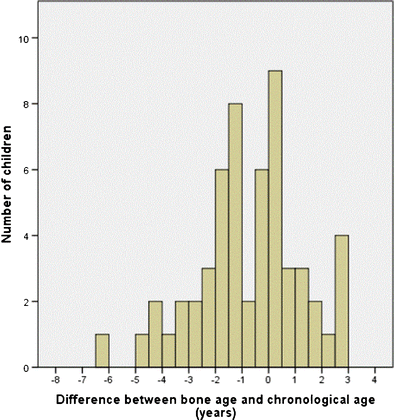
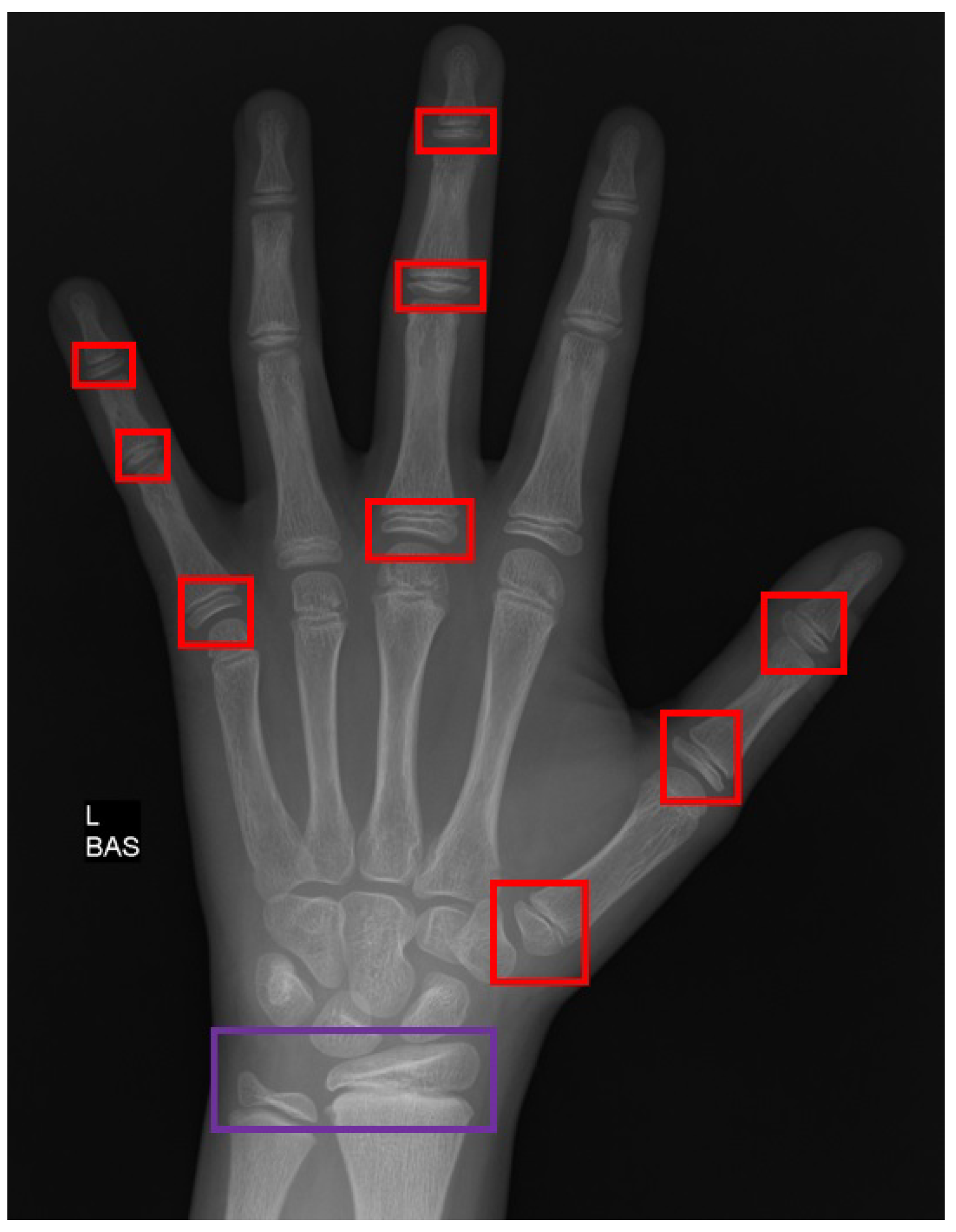
Strong correlation between MR skeletal age and chronological age was observed for both investigators, Pearson correlation R 2 = 0.9 for each. Correlation between chronologic age and MR bone age was determined by means of simple linear regression analysis. Two blinded radiologists evaluated the studies and the following elements were considered: the appearance of cartilage, vacuolization of cartilage, provisional calcification, progression of ossification, and complete ossification. A low field open magnet (0.2 Tesla) was used for this study coronal T1-weighted images with a slice thickness of 1.3 mm were acquired. Materials and MethodsĪ total of 179 (78 female and 101 males, 11 to 16 years old) subjects of 252 normal volunteers met entrance criteria. 29 (3):353-66.To evaluate bone age determination using MRI of the hand and wrist. Novel approaches to short stature therapy. Association between bone turnover markers and bone mineral density in puberty and constitutional delay of growth and puberty.
BONE AGE LESS THAN CHRONOLOGICAL AGE UPDATE
Update of guidelines for the use of growth hormone in children: the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrinology Society Drug and Therapeutics Committee. A review of guidelines for use of growth hormone in pediatric and transition patients. Marked increase of final height by long-term aromatase inhibition in a boy with idiopathic short stature. Krebs A, Moske-Eick O, Doerfer J, Roemer-Pergher C, van der Werf-Grohmann N, Schwab KO. Clinical review: Distinguishing constitutional delay of growth and puberty from isolated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: critical appraisal of available diagnostic tests. Aromatase inhibitors for short stature in male children and adolescents. Use of testosterone gel compared to intramuscular formulation for puberty induction in males with constitutional delay of growth and puberty: a preliminary study. 15 (2):e42311.Ĭhioma L, Papucci G, Fintini D, Cappa M. Testosterone Therapy Improves the First Year Height Velocity in Adolescent Boys with Constitutional Delay of Growth and Puberty.
BONE AGE LESS THAN CHRONOLOGICAL AGE SERIES
Congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, functional hypogonadotropism or constitutional delay of growth and puberty? An analysis of a large patient series from a single tertiary center. Varimo T, Miettinen PJ, Kansakoski J, Raivio T, Hero M. Inhibin B, AMH, but not INS元, IGF1 or DHEAS support differentiation between constitutional delay of growth and puberty and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Rohayem J, Nieschlag E, Kliesch S, Zitzmann M. Delayed puberty versus hypogonadism: a challenge for the pediatrician. 4:6061.īozzola M, Bozzola E, Montalbano C, Stamati FA, Ferrara P, Villani A. Constitutional delay influences the auxological response to growth hormone treatment in children with short stature and growth hormone sufficiency. Gunn KC, Cutfield WS, Hofman PL, Jefferies CA, Albert BB, Gunn AJ. Clinical and Genetic Characterization of a Constitutional Delay of Growth and Puberty Cohort. 476:119-28.īarroso PS, Jorge AAL, Lerario AM, et al. Characteristic dynamics of height and weight in preschool boys with constitutional delay of growth and puberty or hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Reinehr T, Hoffmann E, Rothermel J, Lehrian TJ, Binder G. Progressive Decline in Height Standard Deviation Scores in the First 5 Years of Life Distinguished Idiopathic Growth Hormone Deficiency from Familial Short Stature and Constitutional Delay of Growth. Rothermel J, Lass N, Toschke C, Reinehr T. Constitutional delay of growth and puberty is not commonly associated with mutations in the acid labile subunit gene. 164(5 Suppl):S1-14.e6.īanerjee I, Hanson D, Perveen R, Whatmore A, Black GC, Clayton PE. Etiologies and early diagnosis of short stature and growth failure in children and adolescents. Evaluation of near final height in boys with constitutional delay in growth and puberty. Rohani F, Alai MR, Moradi S, Amirkashani D.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
